Hair transplant techniques have come a long way since the procedure was first performed by a dermatologist in 1952. These days, there are many options for patients to choose from, and differentiating between them can be confusing. The two primary methods of hair replacement are FUE and FUT. While the end result of both procedures is essentially the same (transplantation of individual hair follicles), the extraction process differentiates the two methods.
What is the best choice? What are the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of each? While a patient’s specific situation often determines the best treatment method, a potential hair replacement candidate should understand both options to make the best choice.
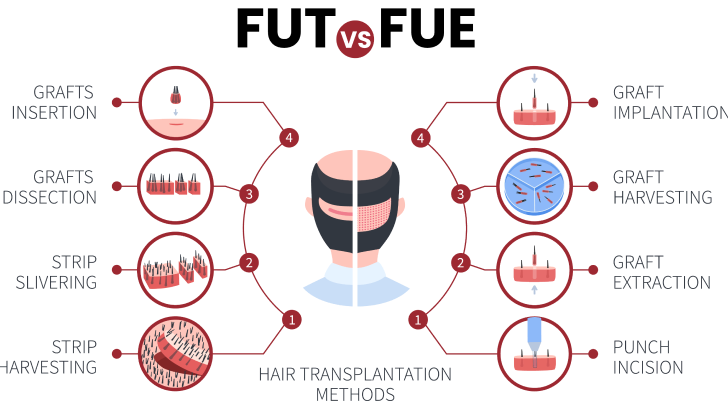
During an FUE procedure, hair follicles are individually harvested from a donor area and implanted into areas where hair is needed. FUE implants leave tiny hypo-pigmented scars in the donor area from the incisions made during harvesting. These scars are typically <1mm and virtually impossible to see when the patient has hair of 2mm or longer.
FUE hair transplants offer two primary advantages over the older strip method.
FUT, or the strip method, is a process by which a long, narrow section of skin is taken from the donor area, followed by follicular extraction of individual follicles via dissection under microscope. Because the strip is taken from the area of greatest concentration, this results in the maximum amount of harvested hair.
The manner in which the strip of donor hair is harvested results in a few potential advantages, but the primary two are:
While an FUT procedure does run the risk of linear scarring in the donor area, an experienced surgeon is often able to leave a scar less than 2 mm in width, and this becomes virtually unnoticeable if the patient wears their hair 4 mm or longer.
Even though it is an older method, FUT does provide exceptional results. Since the method used can depend on many factors, a consultation is needed to determine the optimal technique.
The primary advantage of FUT is this technique’s hair yield. Patients are often able to get the most hair – and some of the best hair – in a single procedure using this method. If a patient requires a significant number of grafts (or desires a fuller head of hair), FUT might be the ideal option. Additionally, when considering the possibility of a second procedure, having an FUT as the initial procedure is a better sequence.
Other critical distinctions between the FUE and FUT methods can be difference-makers for potential patients.
FUE hair replacement is limited by the number of follicles that can be safely extracted and implanted. If a patient needs a significant number of grafts or wants to complete the process in one session, FUT may be the preferred option.
If a patient is exceptionally young and might require additional hair restoration procedures in the future, FUT is usually the better option. Repeat FUT procedures use the same donor area, so scarring is limited to one location while FUE procedures can cause the skin to distort from the tiny scars.
Some doctors utilize modern technological breakthroughs such as the ARTAS® robot for FUE hair transplant procedures, which leverages computer-assisted mapping for better results and accuracy… and automates the laborious process of follicle harvesting and implantation. The FUT method can be time-consuming, as each hair follicle is manually implanted, necessitating more frequent breaks by the doctor and their surgical team.
The team of hair restoration professionals at Hair Center of Nebraska, led by Dr. Daniel Gross, will help you choose the most appropriate hair transplant technique. Call or contact us to schedule your hair loss consultation. Get started on your hair restoration journey today.
1501 Jackson St. #101 Omaha, NE 68102
Subscribe for our monthly newsletter to stay updated